Measurement systems¶
Introduction
At runtime, UNIQO displays the data relating to the physical quantities in the measurement system required by the session locale.
UNIQO natively supports the following measurement systems:
International measurement system
United States Customary System
British Imperial System
Note
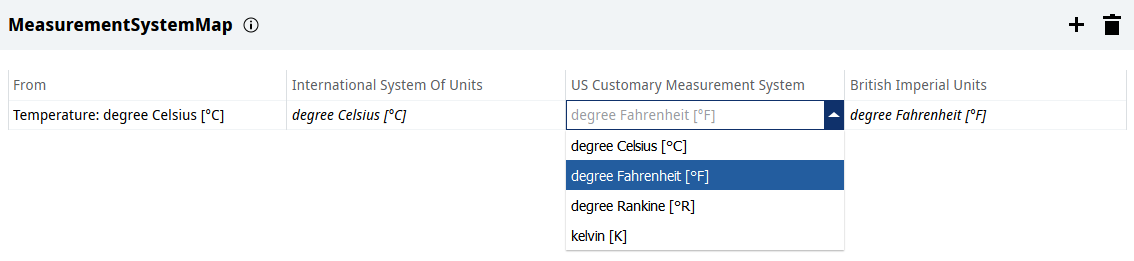
the list of units of measurement in the different measurement systems can be displayed in the MeasurementSystemMap editor. To open the editor, in the project node click  next to the MeasurementSystemMap property.
next to the MeasurementSystemMap property.
Customization of the units of measurement in the measurement systems
If there are no customizations, the session locale determines the measurement system to be used. For example, in a session with en-US locale, the temperature is displayed in degrees Fahrenheit, i.e. according to the United States Customary System.
In UNIQO, through the MeasurementSystemMap editor, the units of measurement to be used in the three measurement systems can be customized at project level for each quantity desired. For example, the representation of temperature in degrees Celsius can also be set for the United States Customary System.
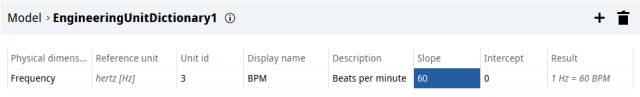
Non-standard unit of measurement
UNIQO supports the units of measurement of the international, US and UK measurement systems. However, it is possible to represent specific quantities of your application through non-standard units of measurement.
For example, the number of pieces produced in one hour in a production process, or the number of beats per minute of a hammer in a control process, etc., can be expressed in non-standard units of measurement. The non-standard units of measurement can be used in the project in the same way as standard units of measurement.
Through the Engineering Unit Dictionary object (see Create non-standard units of measurement), for a reference physical quantity, it is possible to configure new units of measurement whose values depend on the linear relationship that connects the quantities. This relationship is expressed as a straight line with slope and ordinate at the origin:
Slope: conversion coefficient of the non-standard unit with respect to the value of the standard unit
Intercept: additive value of the non-standard unit with respect to the standard unit